PRESS RELEASE
Inapp: “App-dependent businesses: in the catering industry, commissions amount to over 20% for one in three companies. Revenue is depleted for 7 out of 10 companies”
Fadda: “There is a risk of technological, economic and financial dependence of businesses on digital platforms, which recalls, albeit to a reduced extent, the same unbalanced relationship these platforms have with workers. Starting with business rating systems, which entail potential reputational risks, 32 percent of companies in the restaurant industry and 19 percent in the tourism sector have at least once lost customers due to disservices or payment delays caused by the platforms.”
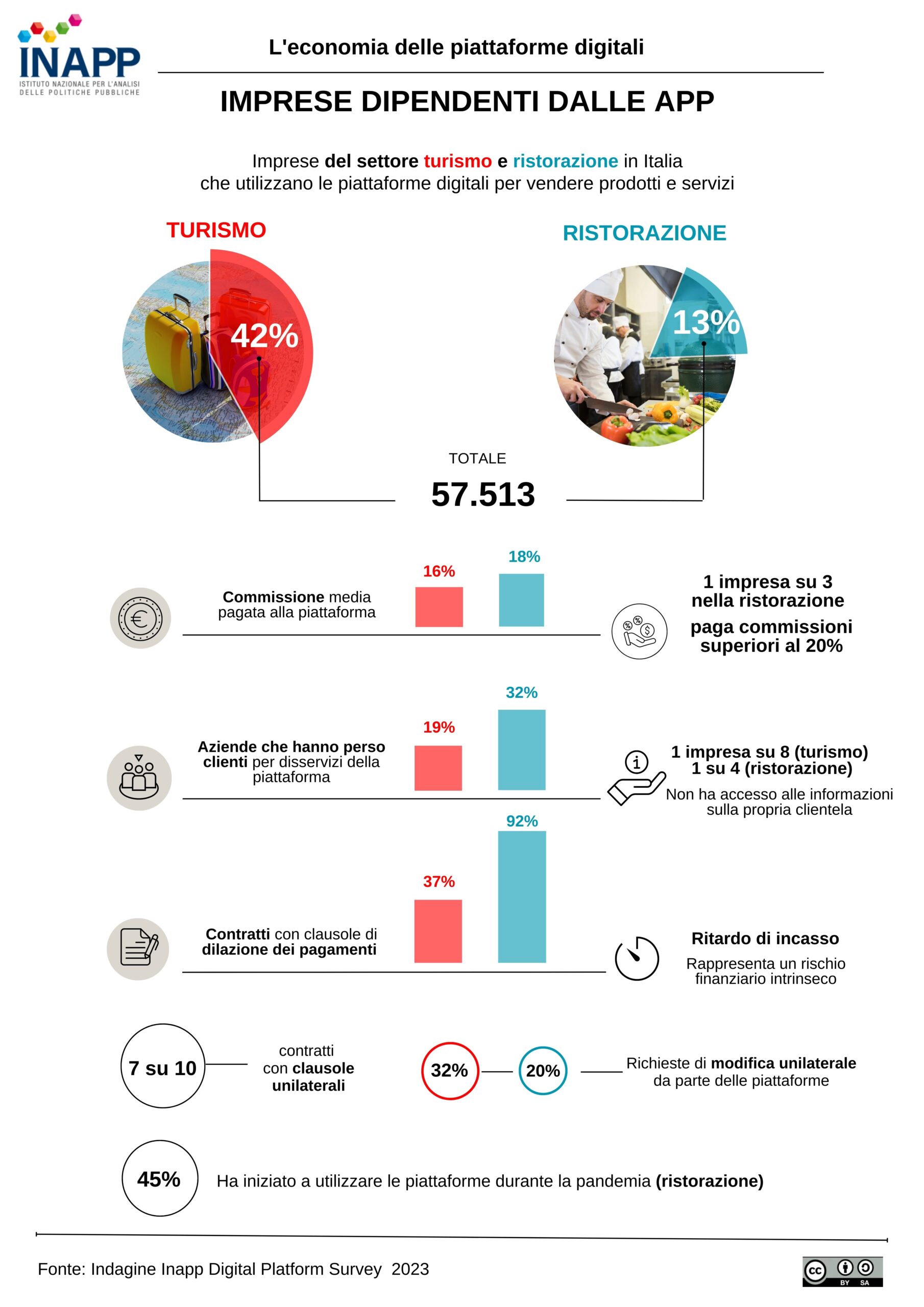
Rome, May 16, 2023 – The average commission that restaurant businesses pay to digital platforms to sell their products is 18 percent, with values above 20 percent for one in three businesses. In tourism, the average commission is 16 percent. Only 1 in 10 businesses pays a fixed commission.
In the restaurant industry, 68% of the contracts with platforms (37% in tourism) include clauses for the collection of payments, and seven times out of ten the contract terms result from the imposition of these unilateral clauses from digital platforms. Similarly, changes to contract terms tend to be unilateral, on the side of digital platforms (32 percent in tourism and 20 percent in catering).
In addition, one in 4 businesses in the restaurant industry do not have access to information about their customers, one in 8 in tourism, with possible repercussions on their market strategies.
These are some of the findings in the “The Economics of Digital Platforms” policy brief presented today by Inapp (National Institute for Public Policy Analysis) at a seminar. The work draws from the “Inapp Digital platform survey,” which for the first time analysed a sample of about 40 thousand companies, including companies with fewer than 3 employees, representative of the 298,991 companies operating in Italy in the restaurant, tourism and transportation sectors in 2022.
“The picture offered by these variables shows the risk of commercial dependence of companies on platforms,” said Professor Sebastiano Fadda, president of Inapp. “Commercial rating systems, which involve potential reputational risks arising from the commercial relationship established with digital platforms, further exacerbate this dependence. 32 percent of companies in the restaurant industry have lost customers, at least once, due to disservice caused by the platforms they work with; and 19 percent in the tourism sector.”
But that is not all. According to the survey, in the restaurant industry, contract clauses that can delay payment transfers from the platform to the business are present in about three-quarters of contracts (37 percent in tourism). This is a significant cost and financial risk factor related to platform payments. The least favourable terms mostly appear in the restaurant sector where in 92 percent of cases platform-mediated payments are delayed in time.
The data above becomes even more striking considering the incidence of the use of digital platforms across the country. In Italy, businesses in the tourism and restaurant sectors that use digital platforms to sell their products and services are more than 57 thousand. The highest share is in the tourism sector with 42% (equal to 38,615 enterprises) and 13% in catering (equal to 18,898 enterprises).
In 2020-2021, the turnover brokered by digital platforms accounted for about half of the turnover in tourism and nearly one-fifth in the catering industry, with average commissions of 16 percent and 18 percent, respectively.
Within the tourism sector, hotels, and bed & breakfasts use digital platforms the most, (around 75-77 percent of the whole sector).
In the restaurant industry, the spread of platform use is more homogeneous. There are more than 13 thousand merchants (13%) who, while carrying out on-site catering, provide take-away services. Higher shares are found among restaurant businesses that do not provide on-site serving, with more than 4,600 operators using digital platforms for takeaway (15 percent).
“While it is true that a significant share of businesses in tourism were already using platforms before 2020,” Fadda commented, “it is also true that for the 45 percent of catering businesses that started using digital platforms for takeaway during the pandemic, an otherwise unknown market space opened up. However, it would be appropriate to rebalance the relationship between platforms and businesses in order not to impose excessive burdens on the latters and consumers.”
As for those companies that do not use digital platforms, about one-third states they do not feel the need to, and another 25 percent because they prefer to manage the relationship with customers in-house. Six percent because of the excessive cost of the service.
For more information:
Giancarlo Salemi – INAPP President Spokesperson (347 6312823)
Allegati
Download the press release